In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing technologies, CNC machining and 3D printing have emerged as two of the most prominent methods for producing parts and prototypes. Each technique offers unique advantages and limitations, making the choice between them dependent on your project’s specific requirements. CNC Machining vs. 3D Printing: Which One is Right for Your Project? Let us have a detail explanation as the below.
CNC Machining vs 3d printing
Overview of CNC Machining and 3d Printing
About CNC Machining
What is CNC Machining ?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a subtractive manufacturing process where material is removed from a solid block (or workpiece) using cutting tools to create the desired shape. It is widely used for metals, plastics, and composite materials and is known for its precision and ability to produce parts with tight tolerances. It is also best feasible act for processing high precise various material assembly components.
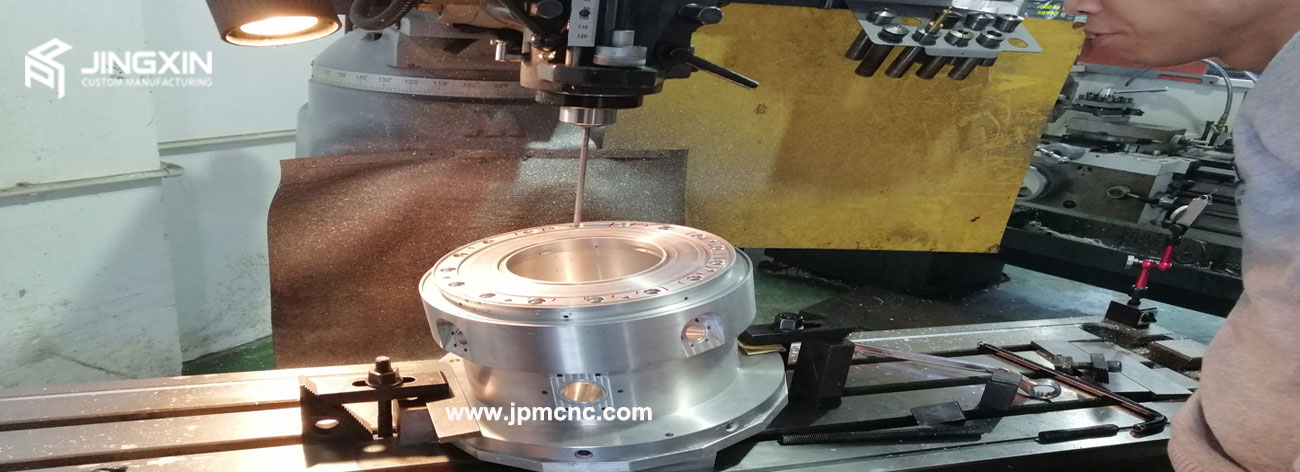

CNC Precision Machining Process
Key Advantages of CNC Machining
- High Precision and Accuracy: Ideal for complex geometries with tight tolerances due to the accurate control from computer system.
- Material Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, and zinc alloys.And cutting the useless slags from the machined part with high hardness tooling steel tool.
- Surface Finish: Produces smooth surfaces and high-quality finishes, often eliminating the need for post-processing. This make the cnc machined components electroplated by nickel, chrome, gold and brass, bring it a perfect appearance.
- Scalability: Excellent for small to medium production runs with consistent quality. It is the process of precision automatication and intelligence integrated into one, can ensure 100% quality standard for each part.
Limitations of CNC Machining
- Material Waste: Subtractive process results in material waste.
- Setup Costs: Initial setup for tooling and programming can be time-consuming and expensive for low-volume runs.
- Design Constraints: Limited in creating intricate internal structures or highly complex geometries.
About 3D Printing
What is 3D Printing ?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds parts layer by layer from digital models, offering unparalleled flexibility in design. It is particularly suited for rapid prototyping and custom, low-volume production.
FDM Rapid prototyping services,3D prototyping services,SLA 3D PRINTING
Key Advantages of 3D Printing
- Design Freedom: Enables creation of highly complex geometries, including internal channels and lattice structures. By computer design software, you can design any imagination geometries freely, with any limitation.
- Material Efficiency: Minimal waste as material is added only where needed. The shape of part is printed by the magic machine, without any redundant material is cut and removed.
- Quick Turnaround: Ideal for rapid prototyping and short production timelines.
- Customization: Easily produces one-off parts or highly customized designs.
Limitations of 3D Printing
- Material Limitations: Restricted to specific materials, often less durable than those used in CNC machining. The printed part is vulnerable because it is formed under high pressure, but saving material.
- Surface Finish: May require additional post-processing for smooth finishes or precise tolerances.
- Strength and Durability: Printed parts may lack the mechanical strength of machined components, depending on the technology and materials used.
- Cost at Scale: Not cost-effective for high-volume production compared to CNC machining. If you need a first prototyping part, it will be lower of your cost largely.
Key Factors to Consider
-
Project Complexity and Design
- Choose 3D printing for intricate designs, internal structures, or lightweight geometries that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with CNC machining.
- Opt for CNC machining when precision and tight tolerances are essential.
-
Material Requirements:
- If your project requires durable, heat-resistant metals like zinc, aluminum, or steel, CNC machining is often the better choice. Some electric components are made of metal material, by die casting, so they should be processed with post process procedure. CNC machining will meet the requirements.
- Use 3D printing for specialized polymers, composites, or lightweight materials where strength is secondary.
-
Volume and Scalability
- CNC machining excels in medium-to-high production volumes with consistent part quality.
- 3D printing is more cost-effective for low-volume production and prototyping.
-
Lead Time:
- For rapid prototyping or projects with short deadlines, 3D printing can provide quick results.
- CNC machining may take longer due to setup and programming requirements but offers consistent quality in repeat production.
-
Cost Efficiency:
- 3D printing is more economical for one-off parts or prototypes.
- For larger production runs, CNC machining offers better cost efficiency per part.
-
Surface Finish and Tolerances:
- For parts requiring smooth finishes and precise dimensions, CNC machining is superior.
- 3D printing may require additional finishing steps to achieve similar results.
Conclusion: Which One is Right for Your Project?
From CNC Machining vs. 3D Printing, we find that the choice between CNC machining and 3D printing depends on your specific project requirements. If you need high precision, durability, and scalability, CNC machining is the go-to method. On the other hand, for innovative designs, rapid prototyping, or cost-effective low-volume production, 3D printing stands out as the ideal solution.
Ultimately, understanding your project’s goals, budget, and timeline will guide you in selecting the right manufacturing process. In some cases, a hybrid approach—leveraging the strengths of both CNC machining and 3D printing—can deliver optimal results.






